Getting Started With Robotics, Microcontrollers and Coding
Programming and robotics support a student-centred, hands-on learning process. Coding and robotics can integrate into your current practice and support students ‘ learning and creativity regardless of what subject(s) you teach. Some robots and microcontrollers require digital devices, but others are screen-free.
What are some robotics and coding tools for the classroom?

Coding Platforms
Coding refers to computer programming. It is the primary language between humans and robots and consists of a set of instructions that will tell a computer or robot what to do. There are several different programming languages Many platforms use drag-and-drop blocks which are great for younger students or as an initiation to coding. Click here for a list of coding platforms and resources.

Robots
In general, a robot is a physical machine or object that is capable of carrying out actions autonomously. Robots can be programmable and have built-in or attached sensors (e.g. distance, temperature, light, inclination). With the use of coding, a robot can change its behaviour or execute a series of actions. Click here for a list of robots and resources.
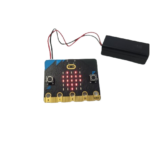
Microcontrollers
A microcontroller is a programmable circuit board that is ideal for special projects. They are great tools for solving specific problems and for animating or controlling toys and tools that you have made. Some microcontrollers even work with fabric so you can animate your clothes! Others can do advanced tasks like checking the weather, watering a plant, or running a website. They are like swiss army knives and are surprisingly common – many can be found in everyday household devices. Click here to see a list of microcontrollers and resources.

Peripherals
These are external devices that can be attached to a digital device to provide enhanced capabilities for example, 3d and vinyl cutters. Click here for a list of peripherals and resources.

Electronic Circuit Kits
Click here to access kits and resources to support student learning related to electricity.

Additional Tech Tools
There are a few tools that don’t clearly fit into the categories above but can be used to enhance curriculum competencies and develop computational thinking. Click here to learn more.
Why should I incorporate robots, microcontrollers and coding in my practice?
Coding and robotics are powerful learning tools to illustrate concepts and apply skills and knowledge in a meaningful and exciting way.
Coding and robotics are great means for integrating STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and mathematics) activities in the classroom, as well as many other subjects such as literacy, history, music, and dance. Students are given the opportunity to work together to develop skills such as communication, collaboration, problem-solving, and critical thinking.
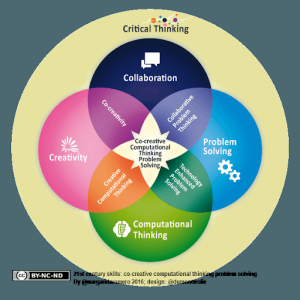
Coding and robotics can contribute to the development of these four crucial 21st Century Skills (Romero & Dupont, 2016):
- Collaboration
- Creativity
- Problem Solving
- Computational Thinking
Coding and robotics activities are also easily tied to the cross-curricular competencies in the Québec Educational Program (QEP) and dimensions of the Digital Competency. Students can develop their creativity and problem-solving abilities throughout the process. By working together, students have the opportunity to improve their social and personal skills.
How do I get started?
Below are some questions that you should ask yourself when preparing to infuse technology in your existing professional practice.

Pedagogy
- What are my pedagogical intentions and goals?
- What do I want students to learn and be able to do?
- What subject-specific and cross-curricular competencies do I want students to develop through educational robotics?
- What activities and projects will support their learning?
- What do my students know about robotics and how do I want to introduce the subject?
Management of Space and Materials
- How should I organize my classroom to facilitate robotics activities and learning?
- How should I organize the different materials?
- Do I want students working in teams or individually for a certain activity?
Digital Devices
- What robots and microcontrollers will best support my pedagogical intention and goal?
- How can different robots and microcontrollers be used to accomplish my goals?
- How will we make time for teachers and students to experiment with the tools and materials?
What support is available?

You do not have to be an expert in robotics to integrate them in your class. You can model problem-solving strategies by working along with your students. If you need support:
- Consult members of your school community – staff, students, parents, local experts
- Get support from your School Board RÉCIT consultants
- Visit our Open Creative Space page
- Check out websites and PD opportunities offered by community partners and the device/software manufacturers , ie. Kids Code Jeunesse
- Attend Provincial Conferences ie. QPAT, LCEEQ, CCI
- Enrol in a Campus RÉCIT training module (French)
- Fill out our PD support form